Cloud Preview
There is typically a significant difference between high-quality media masters and content intended for streaming. Media masters are not only extremely high bitrate, but are often stored in formats (for example, QuickTime ProRes) that are not streamable.
The OptiView Ad Engine can be used to generate cloud-based previews of these media assets, enabling immediate playback without the need to generate or store intermediate proxy files. Previews are created just in time, meaning you only pay for the portions of content you actually view. This is particularly valuable in quality-control (QC) workflows, where reviewers may only need to examine small sections of a longer asset.
Cloud Preview output is compatible with any HLS-capable player. In addition, Dolby provides built-in support for the following multi-track players:
- Codemill Accurate Player — https://www.codemill.com
- Omakase Player — https://player.byomakase.org
Supported Endpoints
The Cloud Preview API exposes three endpoints:
https://api.galaxy.dolbyrasp.com/cloud-preview/hlshttps://api.galaxy.dolbyrasp.com/cloud-preview/codemillhttps://api.galaxy.dolbyrasp.com/cloud-preview/omakase
In the body of your request, you submit a JSON payload that specifies the desired output.
- The HLS endpoint returns a standard M3U8 playlist that can be played in any web-based HLS player.
- The Codemill endpoint returns a JSON template that can be used to launch the Codemill Accurate Player.
- The Omakase endpoint returns a JSON template that can be used to launch the Omakase Player.
Dolby provides hosted versions of these players for testing and evaluation.
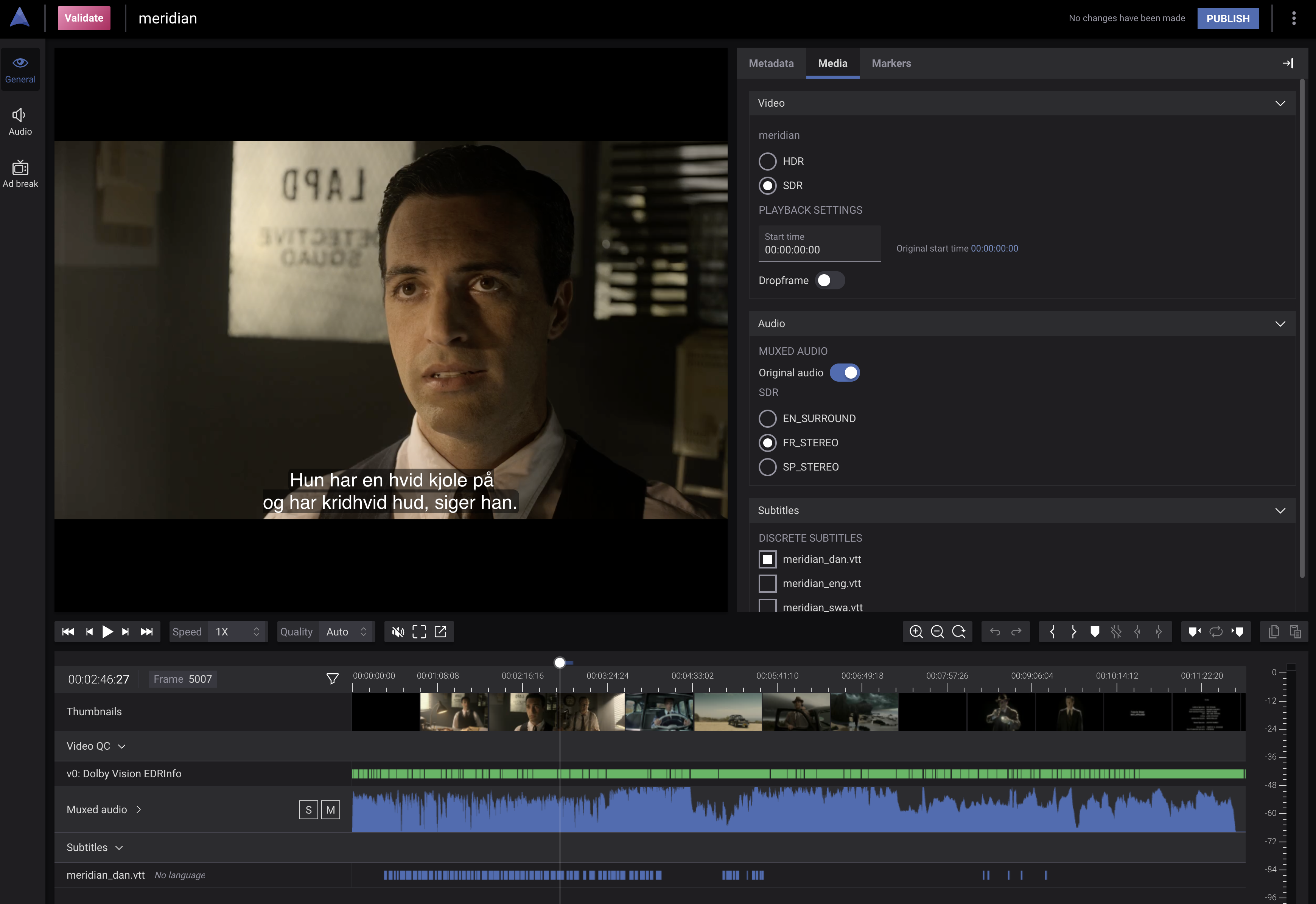
Media Timeline
The Codemill and Omakase players provide a synchronized media timeline that aligns video, audio, and subtitle playback. The Ad Engine generates all supporting assets required for this experience, including thumbnails, waveforms, and HLS media.
The timeline allows users to scrub through content efficiently, validating video quality and verifying audio and subtitle synchronization.
Implicit and Explicit Configuration
The Ad Engine Cloud Preview supports two configuration styles: explicit and implicit.
Explicit Configuration
With an explicit configuration, you know your source files and want to specify exactly how they should be interpreted. For example, if you have a master WAV file containing six mono audio tracks, that audio could represent either a 5.1 surround mix or three stereo language tracks. With explicit configuration, you define precisely how each track should be handled.
Explicit configuration assumes detailed knowledge of the source. If the requested output cannot be created from the provided inputs, the request will fail. For example, if you specify an output that requires audio tracks but the source contains no audio, an error will be returned.
The basic structure of an explicitly configured JSON payload is:
{
"urls": [
],
"map": {
},
"outputs": [
"encode_profile": {
}
],
"options": {
}
}
- urls: The source content to preview, including video, audio, subtitles, metadata, and related assets.
- map: How the source content should be interpreted (for example, which tracks map to which outputs).
- outputs: The outputs to be created (for example, SDR and HDR outputs, multiple languages, or multiple bitrates).
- encode_profile: The encoding parameters applied to each output.
- options: Additional settings that control preview behavior (for example, timecode handling or waveform generation).
Implicit Configuration
With an implicit configuration, the Ad Engine infers mappings and outputs based on the supplied assets and output templates. You define templates with selection criteria, and the Ad Engine determines which templates apply to the provided sources.
This approach is useful when you want a single API call to work across a wide variety of inputs without knowing the source structure in advance. Selectors behave like conditional rules: if the source matches the selector criteria, the corresponding output is created.
In an implicit configuration, you do not need to know how many audio tracks a source contains, or whether certain components are present at all. The output is generated dynamically based on the templates.
The basic structure of an implicitly configured JSON payload is:
{
"urls": [],
"output_templates": [
{
"selectors": [],
"encode_profile": {}
}
],
"options": {}
}
- urls: The source content to preview.
- output_templates: Templates that describe potential outputs.
- selectors: Criteria that determine when a template should be applied.
- encode_profile: Encoding parameters for each template.
- options: Additional preview behavior settings.
Explicit Configuration Example
{
"urls": [
{
"url": "https://my_bucket/my_folder/ProRes_Master_Video.mov",
"id": "v0"
},
{
"url": "https://my_bucket/my_folder/DoVi_metadata.xml",
"id": "m0"
},
{
"url": "https://my_bucket/my_folder/English_stereoe.wav",
"id": "a0"
},
{
"url": "https://my_bucket/my_folder/French_stereo.mov",
"id": "a1"
},
{
"url": "https://my_bucket/my_folder/English_subtitles.stl",
"id": "s0"
}
],
"map": {
"video": [
{
"url_id": "v0",
"dolby_vision_metadata_id": "m0"
}
],
"audio": [
{
"url_id": "a0"
},
{
"url_id": "a1"
}
],
"subtitle": [
{
"url_id": "s0"
}
]
},
"outputs": [
{
"name": "SDR",
"encode_profile": {
"container": {
"kind": "hls/fmp4"
},
"video": {
"height": 720,
"width": 1280,
"bitrate_mode": "crf",
"crf": 19,
"max_bitrate_kb": 8000,
"codec": "h264",
"range": "sdr",
"preset": "veryfast"
},
"audio": [
{
"name": "english",
"language": "eng",
"codec": "aac",
"bitrate_kb": 128,
"channels": 2
},
{
"name": "french",
"language": "fre",
"codec": "aac",
"bitrate_kb": 128,
"channels": 2
}
],
"subtitle": [
{
"name": "subtitle_english",
"codec": "webvtt"
}
]
}
}
],
"options": {
"use_source_start_timecode": true,
"show_dolby_vision_metadate_markers": true
}
}
In this example, the source URL array includes a video file, two audio files, a subtitle file, and a Dolby Vision metadata file. The map section specifies how these sources should be interpreted. For example, the audio configuration defines two output tracks—one English and one French. The outputs section then defines how those inputs are encoded into a streamable preview.
Complex Audio Mapping
The map section can also be used for more complex audio scenarios. For example, consider a case where you have three audio sources: one surround file containing six mono tracks and two additional stereo files. If the desired output consists of one surround track and two stereo tracks, the mapping must explicitly define how individual mono channels are combined.
"map": {
"video": [
{
"url_id": "v0",
"dolby_vision_metadata_id": "m0"
}
],
"audio": [
{
"id": "english_surround",
"channels": [
{
"url_id": "a0",
"track_idx": 0,
"channel_idx": 0
},
{
"url_id": "a0",
"track_idx": 1,
"channel_idx": 0
},
{
"url_id": "a0",
"track_idx": 2,
"channel_idx": 0
},
{
"url_id": "a0",
"track_idx": 3,
"channel_idx": 0
},
{
"url_id": "a0",
"track_idx": 4,
"channel_idx": 0
},
{
"url_id": "a0",
"track_idx": 5,
"channel_idx": 0
}
]
},
{
"url_id": "a1",
"track_idx": 0
},
{
"url_id": "a2",
"track_idx": 0
}
],
"subtitle": [
{
"url_id": "s0"
},
{
"url_id": "s1"
}
]
}
Implicit Configuration Example
In this example, the source assets may include any combination of video, audio, and subtitle files. If the source video is HDR, the templates instruct the system to generate both SDR and Dolby Vision outputs. Audio templates handle mono, stereo, and surround variants, and all subtitle formats are converted to WebVTT. This approach allows Cloud Preview to be used without prior knowledge of the source asset structure. But, if the source was a .wav file with 6 mono tracks, it would always be displayed and played as 6 discrete tracks. In the implicit configuration, you don't have a mechanism to remap discrete tracks into channels - for that you have to use the explicit configuration.
{
"urls": [
{
"url": "https://my_bucket/my_folder/my_video.mov"
},
{
"url": "https://my_bucket/my_folder/English_stereo.wav"
},
{
"url": "https://my_bucket/my_folder/English_subtitles.stl"
}
],
"output_templates": [
{
"type": "video",
"name": "sdr",
"selectors": [
{
"range": "sdr"
},
{
"range": "dolby_vision_5"
},
{
"range": "hdr10"
}
],
"encode_profile": {
"video": {
"height": 720,
"width": 1280,
"bitrate_mode": "crf",
"crf": 19,
"max_bitrate_kb": 8000,
"codec": "h264",
"range": "sdr",
"preset": "veryfast"
}
}
},
{
"type": "video",
"name": "hdr",
"selectors": [
{
"range": "dolby_vision_5"
},
{
"range": "hdr10"
}
],
"encode_profile": {
"video": {
"height": 720,
"width": 1280,
"bitrate_mode": "crf",
"crf": 19,
"max_bitrate_kb": 8000,
"codec": "h265",
"range": "dolby_vision_5",
"preset": "veryfast"
}
}
},
{
"type": "audio",
"selectors": [
{
"channels": 1
}
],
"encode_profile": {
"audio": {
"codec": "aac",
"bitrate_kb": 96,
"channels": 1
}
}
},
{
"type": "audio",
"selectors": [
{
"channels": 2
}
],
"encode_profile": {
"audio": {
"codec": "aac",
"bitrate_kb": 128,
"channels": 2
}
}
},
{
"type": "audio",
"selectors": [
{
"channels": 6
}
],
"encode_profile": {
"audio": {
"codec": "aac",
"bitrate_kb": 256,
"channels": 6
}
}
},
{
"type": "subtitle",
"selectors": [
{
"codec_name": "*"
}
],
"encode_profile": {
"subtitle": {
"codec": "webvtt"
}
}
}
],
"options": {
"use_source_start_timecode": true
}
}